Bitcoin Gains Momentum on the Back of Fed Pivot Narrative, but Some Banks Expect Dollar Rebound
Shortly before press time, Bitcoin went over $20,000, adding to Monday’s “ISM-induced” gains as the dollar continued to fall.
The price of Bitcoin (BTC) is gaining bullish momentum as investors hope that financial stability concerns and signs of an economic slowdown will force the Federal Reserve to abandon aggressive liquidity withdrawal measures.
Some observers, however, are skeptical that the Fed will abandon or significantly slow the so-called liquidity tightening anytime soon, which is why they anticipate renewed dollar strength.
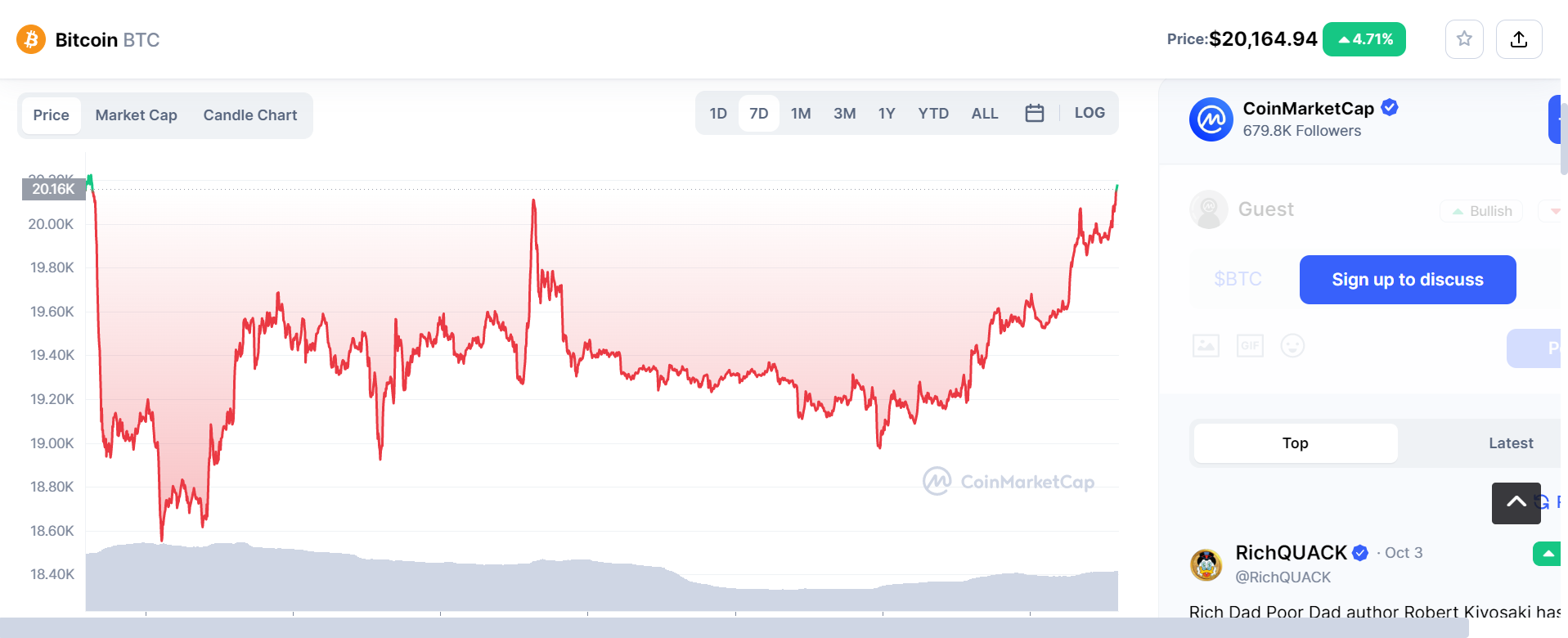

The top cryptocurrency by market capitalization reached a high of $20,160 shortly before press time, a 2% gain for the day. The dollar index dropped to a nine-day low of 11, after reaching a two-decade high of 114.77 on September 28.
On Monday, bitcoin buyers stepped in after the United States Institute of Supply Management (ISM) reported that its manufacturing purchasing managers’ index (PMI) fell to 50.9 in September, the lowest reading since May 2020, from 52.8 in August. Notably, the index’s new orders and employment measures fell, supporting the Fed’s pivot.
The Bank of New Zealand’s research team wrote to clients early Tuesday: “The market has treated the downside surprise to the ISM index as increasing the chances of an earlier Fed pause, which is seen as positive for risk assets.” Even though the Fed raised interest rates by 300 basis points this year, the market value of bitcoin has dropped by half. Bitcoin tends to move in lockstep with stocks.
Last week, the market was filled with hopes that the Fed and other major central banks would slow down on tightening. This was because the Bank of England (BOE) had just announced a bond-buying program, also called “quantitative easing,” to keep the government bond market running smoothly.
“What the Bank of England did was a model for what others are likely to do,” Yardeni Research president Ed Yardeni told Bloomberg. “In the past, a rising dollar has been blamed for causing a global financial crisis. We need to look at this from a global perspective. “
Fed funds futures
Futures trading in federal funds suggests that traders are pricing in rate cuts beginning in May 2023. While the market still expects another 75 basis point (0.75 percentage point) rate hike next month, the terminal rate-the expected high point for this interest rate-hiking cycle-has dropped to 4.4% from 4.75%.
However, ING analysts believe that the central bank’s fight against inflation is far from over.
“Markets smell blood in the water, but do they have enough evidence to price a policy shift? Not yet, in our opinion, “analysts at ING wrote in a client note. “The Bank of England’s reluctance to buy gilts [UK government bonds] shows that it is still fighting inflation.”
Some Fed speakers have been worried about the effects of a stronger dollar recently, but ING analysts think that the current state of the economy does not call for a change in policy.
“Despite slightly weaker-than-expected ISM manufacturing figures yesterday, the domestic story in the United States remains rather solid, keeping Fed tightening prospects alive even if markets have recently revised the expected terminal rate to sub-4.50% levels,” analysts wrote in a note explaining why the dollar’s pullback may not last.
Analysts added that Friday’s non-farm payrolls (NFP) report—the Labor Department’s monthly jobs report for September—could result in a hawkish or pro-tightening repricing of Fed expectations.
Swedbank’s Chief FX Strategist, Anders Eklof, said in a daily note that the recent rise in risk assets is mostly due to the BOE’s intervention in an oversold market, and that it may not last.
“A weaker-than-expected US NFP is required to keep the rally going. The best guess is that the dollar will be bought back soon “Eklof took note.

